Chronic diseases are a major concern in the United States, with conditions like heart problems, cancer, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes causing the majority of deaths. The healthcare system is struggling to keep up with the increasing number of patients, especially with over 400,000 healthcare workers leaving the industry due to the Covid-19 pandemic. This has put immense pressure on the remaining workforce, leading to challenges in providing effective care to those in need.
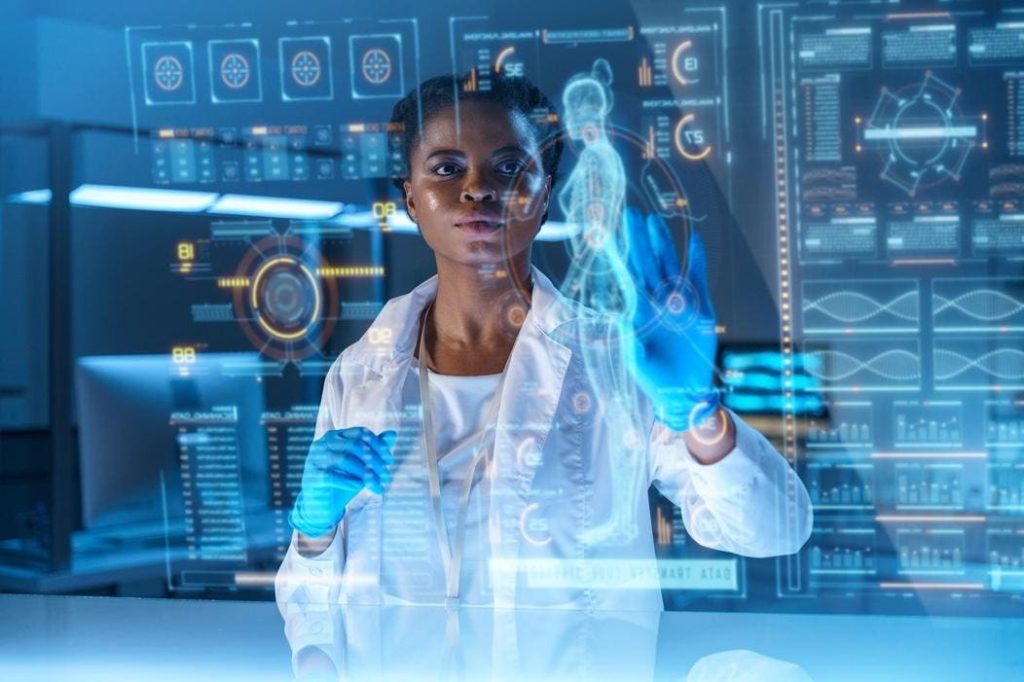
To address the issue of diagnosis errors and improve clinical outcomes, AI is being introduced into healthcare. AI technology can analyze medical reports faster and more accurately than humans, potentially diagnosing rare conditions that may go unnoticed by traditional methods. By utilizing high-quality visual data and advanced machine learning algorithms, AI can identify intricate patterns within patient samples, leading to a more precise prediction of conditions. This can be especially beneficial for chronic diseases that require accurate detection for long-term care.
The use of AI in diagnostics can reduce the workload on healthcare providers, allowing for faster and more accurate diagnosis processes. AI models can work continuously without fatigue, providing consistent results for all samples. This can lead to better patient outcomes, with individuals receiving timely diagnoses that enable them to start treatment sooner. Additionally, AI algorithms can improve healthcare accessibility in underserved populations and regions by automating tasks and empowering non-specialists to undertake complex duties.
AI-driven diagnostics have shown promising results across different medical settings, particularly in the detection of abnormal findings on radiographs, brain tumors, and skin cancer. AI models have been accurate in detecting misplacements of catheters on radiographs, speeding up tumor localization in MRI scans, and outperforming dermatologists in the early detection of skin cancers. While AI tools may not be perfect, they can enhance doctors’ decision-making processes and lead to more precise interventions for patients.
Despite the potential benefits of AI in medical diagnostics, several roadblocks hinder its widespread adoption. Healthcare providers may be hesitant to implement these technologies until their performance is proven in diverse clinical settings. Additionally, obtaining high-quality training data for AI tools can be challenging due to ethical and regulatory restrictions. Policymakers can play a crucial role in facilitating the evaluation of machine learning diagnostic technologies and expanding access to medical data to foster collaboration among stakeholders.
In conclusion, the integration of AI and computer vision technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by transforming patient care, saving lives, and alleviating the financial burden on healthcare systems. While challenges remain in the widespread adoption of AI in diagnostics, stakeholders must collaborate to navigate these obstacles and embrace the full potential of AI to improve healthcare outcomes for all.