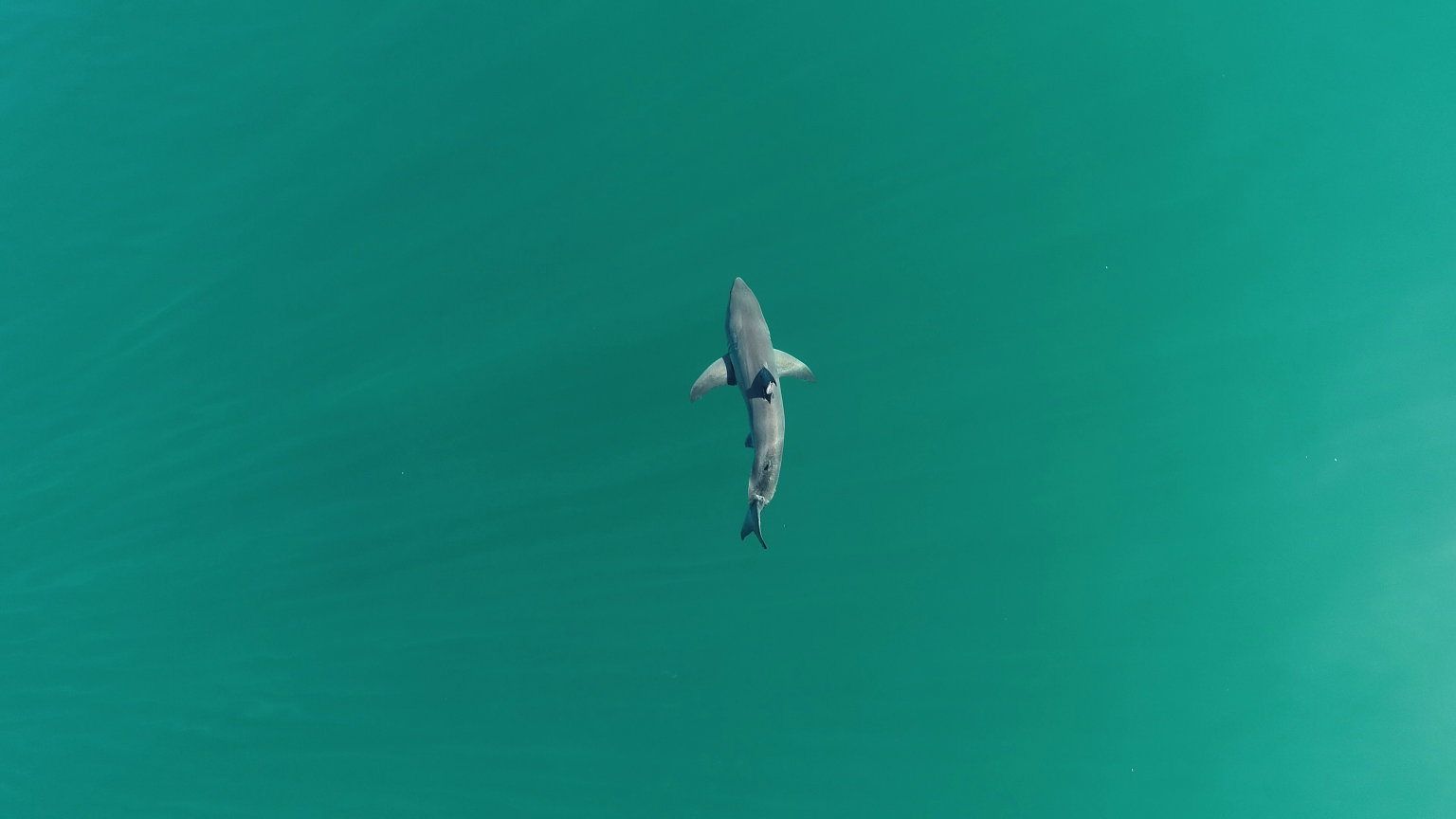
A recent study conducted by marine scientists from California State University, Long Beach, has shed light on the behavior of baby great white sharks. The researchers discovered that juvenile great white sharks prefer to lurk in shallow waters close to the shore, providing an insight into their elusive nursery areas. These findings, published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, are essential for both research purposes and conservation efforts, as they can help protect the public from potential negative shark encounters on beaches in California. The study also highlighted the influence of environmental conditions on the movements of juvenile great white sharks, particularly their preference for specific water temperatures.
To gather data for their study, the researchers tracked 22 young great white sharks using sensor transmitters over a period of two years. By recording water pressure and temperature, the scientists were able to gain valuable insights into the behavior of these sharks. The study revealed that juvenile great white sharks adjust their vertical position in the water column to maintain temperatures between 16 and 22°C, with a preference for temperatures between 20 and 22°C. This temperature range is believed to maximize growth efficiency within the nursery area. The sharks were observed to go deepest during dawn and dusk and stay closer to the surface in the afternoons when the temperature peaked.
The study emphasized the significance of water temperature in attracting juvenile great white sharks to specific locations. While the water temperature plays a crucial role, there are other environmental factors that also influence their movements. Future research will explore individual relationships among sharks to determine if some individuals move among multiple nursery areas. Finding suitable nursery areas is essential for baby great white sharks, as they need protected bays to avoid predators until they can survive in the open ocean. These nurseries must be characterized by the frequent occurrence of young white sharks, prolonged use over several years, and repeated visits by multiple individuals.
The discovery of the nursery behavior of young great white sharks provides valuable insights into their elusive nature and aids in ongoing conservation efforts. While great white sharks remain a mysterious species, progress is being made in understanding their behavior and habitat preferences. Recent sightings of live baby great white sharks in California have added to the growing body of knowledge about these sharks. This study contributes to the collective efforts of scientists in unraveling the mysteries surrounding great white sharks, including their mating rituals and birthing processes. As research continues, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of these iconic marine predators and the important role they play in their ecosystems.
Overall, the study offers new insights into the behavior of baby great white sharks, particularly their preference for shallow waters close to the shore. By uncovering key factors that influence the movements of juvenile great white sharks, researchers hope to improve conservation efforts and reduce potential negative interactions between sharks and humans on beaches. As scientists continue to explore the mysterious world of great white sharks, each new discovery brings us closer to unraveling the mysteries of these iconic marine predators.